VWAP trading strategy, or volume-weighted average price, is a measure of the average price traded throughout the day based on both price and trading volume. This indicator helps traders understand where the current price stands relative to the market’s average level. VWAP is especially useful in intraday trading, where timing and execution efficiency are critical.
In this article, Pfinsight.net explains what VWAP is, how it is calculated, why it is widely used, and how traders apply VWAP trading strategies in real market conditions.
- What is the ATR Indicator and how it works in trading
- How to use Parabolic SAR in Trend-Following trading
- RSI indicator common errors beginners often overlook
What is VWAP trading strategy
The VWAP trading strategy refers to an indicator that measures the average price of an asset throughout a trading session, taking both price and volume into account. Unlike simple moving averages that rely only on closing prices, VWAP more accurately reflects the price levels at which the market has actually traded during the day.
In trading, VWAP is commonly used as an intraday reference point to assess whether the current price is trading above or below the session’s average price. When the price is above VWAP, the market is generally considered to be trading at a premium relative to the average. When price is below VWAP, it is viewed as trading at a discount.
Because VWAP is recalculated continuously during the session and resets each day, it is particularly well suited for intraday trading. For this reason, VWAP is widely used by both retail and institutional traders to analyze price behavior and support short-term trading decisions.
How VWAP is calculated
The VWAP trading strategy is calculated using intraday price data and trading volume, and it is continuously updated throughout the session. This means VWAP only reflects trading activity within the current day and resets at the start of a new session.
The VWAP calculation begins by determining the typical price for each candle or time interval, which is usually calculated as the average of the high, low, and close prices. This price is then multiplied by the trading volume to represent the level of market participation at that moment.
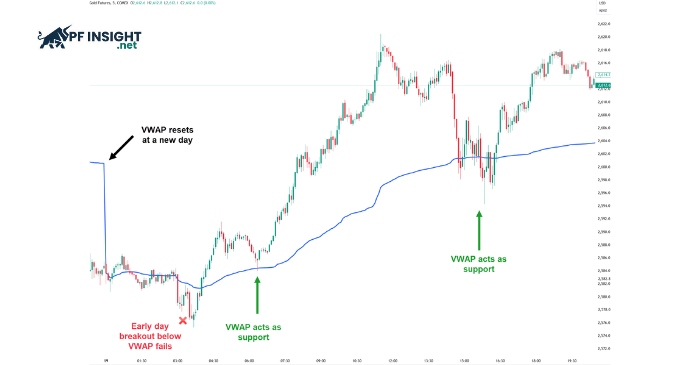
Next, the cumulative total of price multiplied by volume is summed over time and divided by the cumulative trading volume. The result is the VWAP line, which represents the volume-weighted average price of the market throughout the session.
Because of this calculation method, VWAP more accurately reflects the price levels where most trading volume has occurred, rather than relying solely on raw price movement.
Why VWAP is important in trading
VWAP is widely used by intraday traders because it offers several important advantages:
- Identifying the intraday average price: VWAP provides a clear reference point for traders to assess whether the current price is trading above or below the session’s average level.
- Supporting entry and exit decisions: By comparing price action with VWAP, traders can identify more logical entry and exit points in intraday trading.
- Reflecting real market trading behavior: Because it is calculated using both price and volume, VWAP more accurately represents the price levels where the majority of trading activity has occurred.
- Used by institutional traders as a benchmark: VWAP is commonly used to evaluate execution quality, which gives this level meaningful influence on intraday price behavior.
- Useful in ranging market conditions: When the market is moving sideways, VWAP often acts as a fair value zone where price tends to react or revert.
VWAP trading strategy explained
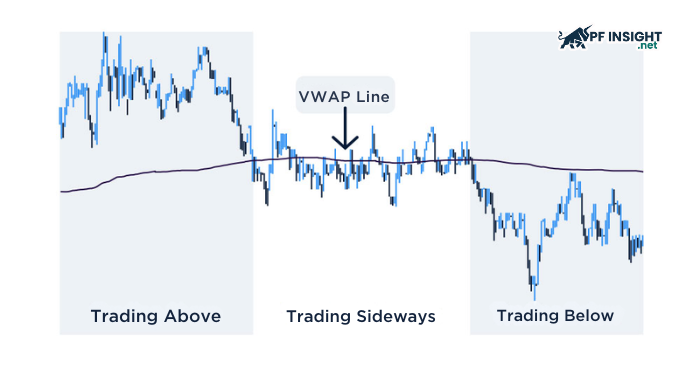
In intraday trading, VWAP should not be treated as a standalone buy or sell signal. Instead, it serves as an anchor point for assessing the market’s condition during the session. Whether the price is trading above or below VWAP helps traders gauge whether buyers or sellers are in control.
One of VWAP’s core strengths lies in its ability to standardize trading context. By observing how price behaves around VWAP, traders can assess whether short-term movements reflect balance or imbalance between supply and demand within the session. This is especially useful when the market lacks a clear trend.
In trending sessions, VWAP is often used as a dynamic reference level rather than a reversal zone. When price consistently holds on one side of VWAP, it suggests that order flow is being absorbed in a specific direction, helping traders avoid trading against the market’s primary momentum.
Because each trading session has a different structure, a VWAP trading strategy is not a fixed set of rules. The effectiveness of VWAP depends on how traders interpret price position, volume behavior, and session context, as well as how well the indicator is combined with other analytical tools.
Example of using VWAP in intraday trading
Step 1: Identify price position relative to VWAP
This helps traders understand whether the market is leaning toward buyers, sellers, or remaining balanced.
Step 2: Assess the intraday market condition
Whether price holds on one side of VWAP or oscillates around it leads to different entry and exit approaches.
Step 3: Choose an appropriate trading scenario
Entries are often considered on pullbacks toward VWAP, while exits are determined based on price structure and acceptable risk.
Step 4: Manage the trade within the session context
VWAP is used as a directional guide rather than a fixed target for every trade.
Advanced VWAP strategies
Using VWAP as dynamic support and resistance
At a more advanced level, VWAP is no longer viewed as a simple average line but as dynamic intraday support and resistance. When price approaches VWAP from above or below, traders focus on the price reaction to assess whether order flow continues to defend this level. This approach is particularly effective during sessions with high liquidity.
Combining VWAP with market structure
VWAP tends to be more effective when analyzed within the context of market structure. For example, if VWAP aligns with a higher low or lower high in the intraday structure, it can become a key reference level for trade decisions. This combination helps traders avoid using VWAP in isolation.
VWAP deviation bands
Some advanced traders use standard deviation bands around VWAP to evaluate how far price has stretched during the session. When price moves significantly away from VWAP, these deviation zones help determine whether the market is in a trend expansion phase or likely to rotate back toward balance. This approach is more suited to reading price behavior than relying on fixed signals.
VWAP in relation to volume behavior
At a deeper level, VWAP is analyzed alongside changes in trading volume. A move above VWAP accompanied by increasing volume carries a different implication than a breakout occurring with weakening volume. This distinction helps traders differentiate between moves supported by genuine market participation and short term fluctuations.
When advanced VWAP strategies may fail
Even advanced VWAP approaches have limitations. During sessions driven by major news events or characterized by low liquidity, VWAP can lose its role as a reliable reference. For this reason, traders must always evaluate the broader market context before applying these advanced strategies.
Who should use VWAP and who should not
VWAP is not a suitable indicator for every trader or every market condition. Its effectiveness depends heavily on the trading timeframe, liquidity conditions, and the user’s trading objectives.
Who should use VWAP: VWAP is particularly well suited for intraday traders who need a reference point to assess the market’s average price during the session. It is also useful for traders who focus on execution quality, as VWAP helps evaluate whether trades are filled at favorable prices. In addition, VWAP works best in highly liquid markets, where volume data more accurately reflects overall market behavior.
Who should not rely on VWAP: In contrast, VWAP is not ideal for medium or long term traders, since it resets each session and does not reflect broader, longer term trends. In low liquidity or erratic markets, VWAP can be distorted by isolated large-volume transactions. Traders who look for fixed buy and sell signals or strictly mechanical strategies may also struggle with VWAP, as the indicator requires contextual interpretation rather than rigid rules.
Overall, VWAP is better viewed as a decision support tool rather than a complete trading system. Using it effectively requires traders to clearly understand their trading objectives and the specific market conditions they are operating in.
Conclusion
The VWAP trading strategy combines price and volume to help traders assess where the current price stands relative to the market’s intraday average. Rather than providing fixed buy or sell signals, VWAP is used as a reference point to interpret market context and price behavior. An effective VWAP trading strategy depends on how traders read this indicator under different market conditions and how they combine it with appropriate analytical tools.
We hope readers find trading approaches that suit their style and lead to consistent results. Follow and explore more of our articles in the Knowledge Hub.