Investing in financial markets is one of the most profitable investment methods favored by many traders. However, to succeed in trading, investors must carefully consider several factors such as lot size and risk management strategies.
Understanding lot size rules helps traders protect themselves from potential losses while maximizing desired profits. In today’s article, Pfinsight.net will share some effective strategies and tips to help traders determine the right lot size rules for successful trading. Let’s dive in!
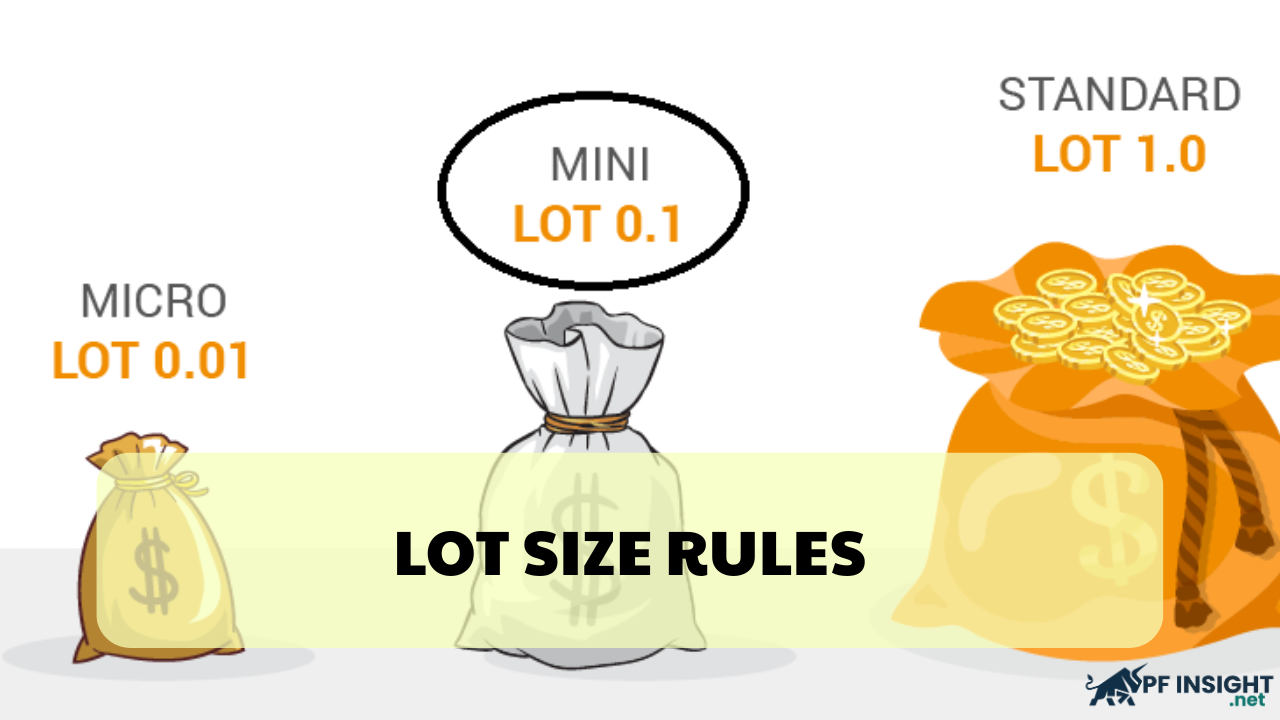
What is lot size in trading?
Lot size refers to the volume of financial instruments that a trader decides to buy or sell in a single transaction. Essentially, it determines the number of units or products involved in each trade.
Lot sizes help ensure consistency in trading by allowing traders to standardize the quantity across different trades.
For example, while 100 shares is considered a standard lot in stock trading, the lot size varies depending on the traded asset in other markets like forex, futures, or bonds.
Understanding lot sizes is crucial because they directly impact the potential profits or losses from a trade.
What are lot size rules in investing?
Depending on the type of asset, different financial markets adopt different lot size rules. Below are some common examples:
Stocks
In the stock market, the standard lot size is usually 100 shares.
For example, when you hear a trader saying they are trading a “lot” of XYZ stock, it typically means they are trading 100 shares at once.
Although odd lots and smaller lot sizes are becoming increasingly common with some brokers, the 100-share lot remains the fundamental benchmark for stock trading.
Bonds
Lot sizes for bonds are significantly larger than those for stocks.
Generally, bond lots are issued with face values starting from $100,000 or more. Many institutional bonds are even traded in multiples of $1 million, compared to the standard 100-share lot in stocks.
However, for retail investors, bond funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs) provide a more accessible way to invest in bonds without needing to purchase such large lot sizes.
Futures contracts
In the futures market, lot sizes are referred to as “contract sizes.” These vary significantly depending on the underlying asset.
Futures contracts can represent bonds, stocks, interest rates, or even commodities.
For example:
- One British pound futures contract is worth 62,500 GBP.
- One Japanese yen futures contract is worth 12,500,000 JPY.
Since futures contracts have fixed lot sizes, traders cannot change the lot size within a single contract.
Forex (Foreign Exchange)
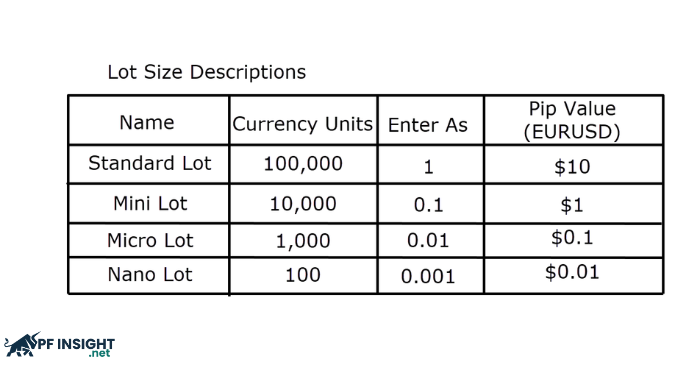
In the forex market, standard lot sizes are also used where currencies are exchanged.
- 1 Standard Lot = 100,000 units of the base currency.
- 1 Mini Lot = 10,000 units.
- 1 Micro Lot = 1,000 units.
These smaller lot sizes allow traders with limited capital to participate in the forex market effectively.
To help traders choose the appropriate lot size based on their account balance, risk tolerance, and trading strategies, most forex brokers provide a lot size calculator.
How to calculate lot size

Effective risk management requires knowing how to determine your trade size. When selecting the appropriate lot size for your trades, you should consider several factors:
Risk tolerance
Different traders have different levels of risk appetite.
A general rule is that you should never risk more than 1% of your total account balance on a single trade.
This approach ensures that even if the trade goes against you, your losses remain manageable.
Account balance
The lot size you choose largely depends on the capital available in your account.
Traders with larger account balances can afford to trade larger lot sizes, but it’s still essential to ensure that your trade size aligns with your risk tolerance.
Stop – loss placement
A stop-loss order is a critical tool for controlling risk.
Your lot size should also be influenced by the distance between your entry price and stop-loss level:
- A tight stop-loss requires a smaller lot size to stay within your risk limits.
- A wider stop-loss allows for larger lot sizes without exceeding acceptable risk levels.
Lot size formula
You can calculate the ideal position size using the formula:
Position Size = Risk Amount ÷ (Stop Loss in Pips × Pip Value)
Example:
If you risk $200 on a trade with a 50-pip stop-loss and the pip value is $10:
Position Size = $200 ÷ (50 × $10) = 0.4 Standard Lots
This method ensures that you never exceed your predefined risk tolerance.
Why lot size rules matter in trading?
Your potential profit and level of risk are directly influenced by the lot size you choose. Selecting the right lot size depends on:
- Your trading strategy
- Your risk tolerance
- Current market conditions
Larger lot sizes increase both profit potential and loss exposure.
For forex traders, understanding the differences between standard lots, mini lots, and micro lots is essential.
Beginners or traders with small accounts are often advised to start with micro or mini lots to minimize risks while gaining experience.
Choosing the correct lot size plays a critical role in both trading success and risk management across all markets – whether you’re trading stocks, bonds, futures, or forex.
Selecting the best lot size for your trading strategy
Choosing the optimal lot size is a key component of any successful trading strategy. It affects both your risk control and profit potential.
When deciding, consider the following:
- Risk Tolerance – Are you comfortable taking risks? Lower risk tolerance typically means using smaller lot sizes.
- Trading Strategy – For strategies like day trading, smaller lot sizes may be better because they allow for quicker entries and exits.
- Market Volatility – In highly volatile markets, smaller lot sizes help reduce exposure. Conversely, stable markets may allow more flexibility.
- Broker Options – Some brokers only offer standard lot sizes, while others support mini, micro, or even nano lots. Always confirm what your broker provides.
By evaluating these factors, you can select the best lot size to match your strategy and preferences while keeping risk under control.
Common mistakes to avoid in lot size and risk management
When determining your lot size, avoid these common mistakes:
- Overleveraging – Using excessive leverage with large lot sizes can cause rapid, uncontrollable losses.
- Ignoring Market Conditions – Failing to adjust lot sizes during volatile market events or news releases may lead to unexpected losses.
- Abandoning Your Trading Plan – Making impulsive decisions based on emotions instead of sticking to your risk management strategy can be costly.
Conclusion
We hope this article has helped you better understand lot size rules in financial trading. Having a clear grasp of lot sizes across different markets allows traders to make informed decisions and build more effective investment strategies. For more insightful trading tips and strategies, don’t forget to visit Pfinsight.net regularly!