Technical analysis is one of the top factors that many traders pay attention to during the trading process because it provides unique signals and indicators that help traders enter positions more easily. Therefore, traders must have solid knowledge, experience, and understanding of fundamental analysis in the market.
But what exactly is fundamental analysis? What does fundamental analysis for traders mean? Let’s explore this in detail with Pfinsight.net through today’s article.
What is fundamental analysis for traders?
The process of analyzing economic, social, and political factors that may affect the price and performance of a financial asset before investing is called fundamental analysis.
This investment strategy allows traders to research companies that produce or provide products and services.
For example, fundamental analysis for traders may include examining the financial situation, financial statements, risks, current management plans, growth forecasts, past product performance trends, and the challenges competitors are facing.
The purpose of fundamental analysis for traders is to determine whether an investment opportunity is currently overvalued or undervalued.
This type of research is an ideal way to evaluate before investing, especially if you discover that an asset you are monitoring is trading at an unusual level and buying it could generate profits. However, even when profit is possible, you must remember that there is also a potential for loss.
How does fundamental analysis work?
Fundamental investors consider a wider range of factors. They take into account how interest rates, politics, and the overall economic situation might affect the cost or value of an asset.
In contrast, technical analysis focuses on charting price movements over time to try to forecast future prices based on historical trends. To determine the ideal time to buy or sell an asset, technical traders use technical indicators such as moving averages, Fibonacci retracements, and support and resistance levels.
What’s the difference between fundamental and technical analysis?
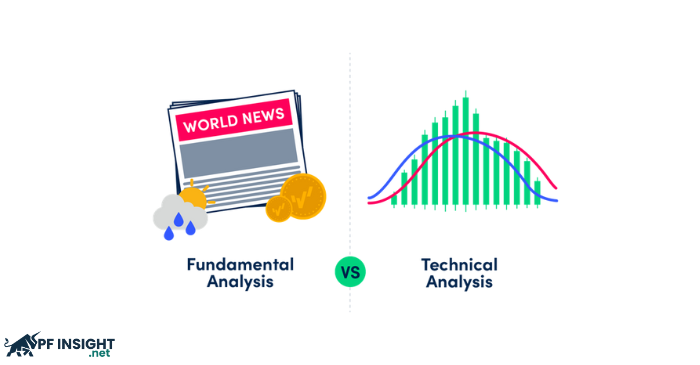
Fundamental analysts look at economic variables affecting an asset’s performance to determine whether it is trading above or below its intrinsic value. Research is conducted from a macro to micro perspective, using publicly available data.
Technical analysts, on the other hand, try to predict future price movements by examining price charts and trading volumes. Technical analysis usually ignores fundamental factors and relies solely on an asset’s previous price and value data.
Technical analysis disregards underlying factors and instead focuses on predicting price direction by analyzing past market data, including price and volume.
While fundamental analysts prioritize identifying long-term potential, technical traders rely on momentum and often open positions within shorter time frames.
What is the difference between quantitative and qualitative fundamental analysis?
Fundamental factors can be divided into two categories: qualitative and quantitative.
- Quantitative fundamental analysis examines various numerical factors, such as market capitalization, interest rate policies, earnings per share (EPS), and other financial ratios. The asset being studied determines which quantitative data is relevant. Profitability is then assessed by comparing these figures with industry averages or other benchmark tools.
- Qualitative fundamental analysis, on the other hand, focuses on factors like management competence, brand recognition, corporate leadership, and unique technology. In this type of analysis, the quality and relevance of these factors play a more significant role than purely numerical data, such as revenue or profit margins.
Many fundamental analysts believe that combining qualitative and quantitative analysis provides a more comprehensive understanding of an asset.
What are the advantages of fundamental analysis?
Fundamental analysis for traders is currently one of the most widely used methods for making financial decisions, offering numerous benefits.
Many investors are drawn to fundamental research because it provides a more accurate picture of market conditions and, therefore, offers better signals for trading opportunities. However, due to the inherently high risks of financial markets, conclusions drawn from fundamental research are not always entirely reliable.
Some key advantages include:
- Since fundamental analysis relies on studying long-term patterns, it is highly recommended for long-term investing.
- When used to predict the best investments, fundamental analysis can be a profitable tool. These forecasts are generated before investors need to make investment decisions.
- The impact on an asset’s value is greater if the information comes from credible and reputable sources.
- Investors can select the best companies and avoid those that are financially vulnerable by analyzing earnings and earnings forecasts, which can provide valuable insights into a company’s growth potential.
What are the disadvantages of fundamental analysis?

Despite its benefits, fundamental analysis also has several drawbacks. One of the main limitations is that it can significantly prolong the decision-making process since it requires substantial time and resources to gather all available information about an asset.
Another disadvantage is that this type of research can sometimes overlook profitability because it does not always consider the impact of market sentiment on prices.
Some major drawbacks include:
- Analyzing balance sheets, cash flows, and financial reports in detail is necessary but can be challenging for investors. A trader may open a disastrous position if these documents are misrepresented.
- Unlike technical analysis, which often provides clear buy and sell signals, fundamental analysis does not offer such straightforward guidance.
- Fundamental analysis is a comprehensive approach to evaluating currency price patterns, but many short-term trading goals and strategies cannot rely on it since it primarily focuses on long-term investments.
- Traders must conduct thorough due diligence and possess deep knowledge of the industry, economy, and competitors related to the asset under study. When markets move quickly, this approach can be time-consuming, and the insights gained may not always be practical.
How to perform fundamental analysis for traders?
For example, in the foreign exchange (forex) market, selecting a currency pair to analyze is the first step in conducting fundamental analysis.
Most of the fundamental information you need is provided by government institutions and can often be accessed online or through an economic calendar.
Key fundamental data that traders frequently examine include:
- Trade balance data
- Microeconomic indicators
- GDP figures
- Annual reports
- Current economic conditions
- Employment statistics
The ultimate goal of fundamental analysis is to assess the current state of a country’s economy and evaluate its growth potential. When conducting fundamental analysis, here are several important factors to consider:
Is the country’s economy growing?
By examining a country’s GDP growth over the last four quarters, you can determine whether it is experiencing steady growth or decline. Consistent GDP growth indicates a healthy economy, while slower growth may suggest underperformance.
What are the Central Bank interest rates?
Interest rates set by central banks vary depending on whether a country is developed or developing.
For instance, since the 2008 global financial crisis, interest rates have remained extremely low in most developed countries but remain relatively high in many developing nations.
Generally, higher interest rates indicate that the central bank has confidence in the economy. Conversely, lower rates may signal weaker economic performance.
Is inflation rising?
The level of inflation in a country is a reliable indicator of purchasing power, reflecting whether the economy is strong or weak. Generally, those with more money enjoy better living conditions than those with less.
Data from the Consumer Price Index (CPI) is widely considered a reliable measure of inflation.
How stable is the country’s political environment?
You can assess a country’s political stability by examining both recent elections and the current political climate. Developing countries with peaceful elections are typically considered more politically stable than those with disputed or violent elections. In contrast, developed countries often exhibit political stability supported by strong judicial systems and consistent governance.
What is the employment situation?
How does the country’s current unemployment rate compare with historical data? Are wages for the workforce rising? Countries with low unemployment rates and significant income growth tend to have stronger-performing economies than those with high unemployment and stagnant wages. Employment statistics, unemployment rates, and jobless claims are considered highly relevant in fundamental analysis.
Conclusion
The above covers all the essential information about the fundamental analysis for traders method that we have compiled. Hopefully, through this article, you now have a comprehensive overview and a clearer understanding of how to perform fundamental analysis in investing.
Don’t forget to visit our website regularly to stay updated with more valuable trading insights and market information!