Algorithmic trading system use technology to automate the entire trading process, from data analysis to order execution. This approach focuses on speed, accuracy, and the ability to process large amounts of information that humans can hardly achieve. In this article, PF Insight will analyze how algorithmic trading works and the advantages.
- Scalping trading techniques tools that improve execution speed
- Position trading strategy how long term traders follow major trends
- Swing trading strategies how to balance risk and reward effectively
What is algorithmic trading?
Algorithmic trading system is a form of trading in which a computer automatically executes orders based on a predetermined set of algorithms. This method is also known as automated trading or black box trading. In theory, this automation allows the system to exploit market opportunities faster and more frequently than humans.
The scripts in algorithmic trading systems are usually based on rules such as time, price, volume or certain mathematical models. Not only does it help traders find profits, this form of trading also contributes to increasing market liquidity and bringing consistency in trading by eliminating the influence of human emotions.
How does an algorithmic trading system work?
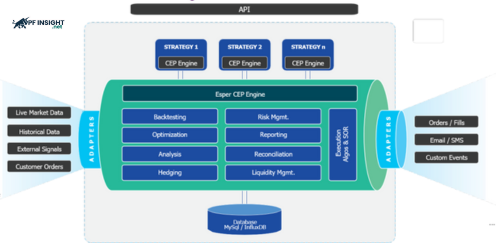
In algorithmic trading systems, computer programs automatically process and execute trades based on fixed rules. These systems work best in high-speed markets such as stocks, forex, and commodities. The advantage of algorithmic trading is that it helps traders eliminate emotions, improve execution efficiency, and maintain accurate strategies without constant monitoring.
Pre-programmed trading conditions are often based on technical indicators, volume fluctuations or complex mathematical models. When these conditions appear, the algorithm immediately sends trading orders to take advantage of the opportunity immediately. Thanks to live data feeds, automation systems and strong internet connections, algorithms can respond extremely quickly to market changes.
Algo trading classifications
Algorithmic trading systems are divided into the following 5 main groups:
TWAP (Time weighted average price) algorithm
TWAP, or time-weighted average price, is a trading algorithm that aims to achieve an execution price that is close to the average price of a security over time. The algorithm works by splitting a large order into several smaller orders of similar size and executing them at regular intervals. The goal of TWAP is to minimize market impact and ensure a steady flow of transactions, avoiding erratic price fluctuations.
VWAP (Volume weighted average price) algorithm
VWAP is an algorithm that calculates the average price of an asset during the trading day, taking into account the volume at each price point. This is the reference standard that many traders rely on to evaluate the effectiveness of their trading orders. If the price is better than VWAP, it is considered a trade with an advantage compared to the general market.
POV (Percentage of volume) algorithm
The percentage of volume algorithm is designed to match orders based on a predetermined percentage of the total volume traded in the market. As the market changes, the algorithm automatically adjusts the execution speed to limit the impact on price. This makes the trading process more natural and less volatile.
Impact driven algorithms
Algorithmic trading system optimizes market impact by splitting large orders into multiple smaller orders, which reduces price volatility and avoids market disruption.
Cost driven algorithms
This algorithmic trading system is cost-based and adjusts execution according to real-time market data, optimizing the balance between transaction costs and execution quality.
Advantages and disadvantages of algorithmic trading system

Algorithmic trading systems have their own strengths and limitations that traders need to consider before applying.
Advantage
- Minimizing price impact: When a large order appears, it can significantly move the price. Algorithmic trading systems handle this by breaking the order into smaller parts and executing them gradually, reducing market attention and minimizing the effect on price fluctuations.
- Optimal execution price: By analyzing real-time market data along with historical patterns, the algorithm can identify the best entry and exit points, helping traders achieve more favorable prices when buying or selling.
- Superior speed: With the ability to process data extremely quickly, algorithmic trading systems respond instantly to market movements, allowing traders to capture opportunities that manual trading cannot match.
- Enhanced consistency: When all decisions are made automatically based on data, trading becomes more stable and reliable. Emotions are removed from the process, reducing errors and improving long-term performance.
Disadvantages
- Market volatility risk: Breaking large orders into smaller parts helps reduce price impact but extends execution time. During this period, market conditions may change, increasing risk for the trader.
- Market manipulation: Other traders, especially well-capitalized institutions, can analyze and detect the system’s patterns. Once they understand the algorithm’s reaction model, manipulating prices to the trader’s disadvantage is entirely possible.
- Technology dependence: Algorithmic trading systems rely entirely on accurate systems and data. Any technical failure, from server issues to connectivity loss, can result in significant losses for the trader.
- No guarantee of order completion: For algorithms like POV, completing the full order volume is not always certain, particularly when market liquidity is limited or multiple competing orders exist simultaneously.
Guide to algorithmic trading for beginners
Algorithmic trading system is performed in the following 6 steps:
Step 1: Choose a strategy that suits your goals and trading style
The first important step in an algorithmic trading system is to choose and define a specific trading strategy, with a clear analytical basis. Traders need to determine profit targets, acceptable risk levels and appropriate asset groups. Once you have a direction, develop a complete plan, showing the strategy logic, entry and exit conditions and money management rules to be followed.
- Entry and exit criteria
- Position sizing plan
- Risk management rules to follow
- Performance evaluation metrics for the strategy
Step 2: Choose trading tools and platforms
There are many platforms you can use to program, simulate, and run trading algorithms. These tools streamline the strategy development process and are used by many algorithmic traders.
- MetaTrader: This is a popular platform in Forex and CFD trading, supporting programming of automated strategies through the MQL language, allowing traders to easily create, test and deploy trading algorithms.
- QuantConnect: A cloud-based platform that enables algorithm development in multiple languages like Python or C#, while supporting testing on high-quality data.
- Interactive Brokers: Provides a powerful API system for automated trading, comes with a backtesting toolkit and reliable order execution.
- NinjaTrader: Fully featured to build, simulate and optimize trading strategies, suitable for both manual and algorithmic traders.
Step 3: Choose a programming language
Developing an algorithmic trading system requires basic programming knowledge. Traders typically use Python, C++, Java, C#, R, or MQL to write strategies, analyze data, and automate order execution in the market.
- MQL: MetaTrader-specific programming language, used to build trading robots, custom indicators and strategy automation.
- Java: A powerful and stable choice, suitable for high-speed trading systems thanks to its multi-threading capabilities and high security.
- Python: Data analysis and strategy development is made simple with a rich library ecosystem like Pandas, NumPy, TA-Lib, and many other supporting tools.
- R: Suitable for complex statistical models and in-depth data analysis, although its popularity in algorithmic trading is not as strong as Python.
- C++: Offers superior processing speed, well suited for high-frequency trading (HFT) systems, but requires advanced programming knowledge and longer development time.
Having programming skills allows you to proactively build trading logic, optimize execution processes, and set precise risk management rules. At the same time, you can implement advanced strategies such as machine learning, API connectivity, and real-time market data processing.
Step 4: Conduct a backtest of the strategy
Once you have built your algorithmic trading system, you need to backtest it using historical market data. This simulation helps you evaluate the strategy’s efficiency, stability, and profitability. For reliable results, make sure your backtest includes high-quality data, transaction fee parameters, and real-world market conditions.
- Data Quality: Make sure the historical data you use is clean, reliable, and noise-free to avoid misleading backtest results.
- Out-of-sample testing: Evaluate the algorithm on datasets it has not been exposed to before to verify stability and adaptability.
- Walk-Forward Analysis: Perform phased optimization and continuous performance testing to ensure the strategy remains effective in changing market conditions.
Step 5: Test Paper trading
Before risking real capital, you should test your algorithmic trading system on paper trading to simulate real market performance. This method allows you to evaluate performance, detect errors and adjust your strategy in a completely risk-free environment. This is an important step to ensure that the system is ready for live trading.
Step 6: Start trading with real capital
Once your algorithmic trading system has been validated through testing, you can move on to live trading. Start with a small amount of capital to get used to the real market, then gradually increase it when your performance is stable. Closely monitor your trading results to optimize your strategy as needed.
Top 5 most effective algorithmic trading strategies
Algorithmic trading systems include many different strategies, from simple to complex, depending on the goals and risk tolerance of each trader. Below are popular and widely used strategies.

Trend following strategies
Trend-following strategies use price data and technical indicators such as moving averages, breakouts, or volatility levels to determine market direction. Once an uptrend or downtrend is detected, the algorithm executes appropriate orders, aiming to profit from long-term strong uptrends and downtrends.
For example: Open a buy order for EUR/USD when the price breaks above the 20-day price channel and closes above the nearest resistance level, confirming a new uptrend.
Statistical arbitrage strategies
Statistical arbitrage takes advantage of statistical price differences. When an asset’s price deviates from its expected average, the algorithm opens an order in the opposite direction of the movement, waiting for the price to retrace back to the benchmark to make a profit.
A common example is a pairs trading strategy, which relies on the long-term correlation between two stocks. When the price difference moves too far from the average, the system buys the weaker stock and sells the stronger stock, waiting for the difference to return to normal. Advanced models can scale to multiple groups of stocks, using clustering and co-integration techniques to find statistical deviations. With automation, the strategy can run continuously, optimizing both analysis and execution.
Arbitrage strategies
Arbitrage strategies use algorithms to detect and exploit temporary price discrepancies between exchanges or correlated financial products. When a discrepancy occurs, the system immediately buys and sells simultaneously to lock in profits.
For example, if Bitcoin is trading at $42,000 on exchange A but $42,180 on exchange B, the algorithm will simultaneously buy on exchange A and sell on exchange B to take advantage of the price difference.
Momentum strategies
The Momentum strategy is based on the principle that assets that have risen will continue to rise and assets that have fallen will continue to fall. By tracking the speed and strength of the trend, the algorithm buys when momentum is strong and sells when momentum is weak. The strategy’s profits are generated by crowd psychology, where traders are often slow to react or are influenced by emotions, causing prices to move sharply away from equilibrium. Momentum exploits this persistence to create a trading advantage.
The biggest challenge with momentum strategies is that trends can reverse suddenly, causing a sharp drop in performance and volatility in accounts. Therefore, it is extremely important to accurately determine the timing of entry and exit. Traders must apply strict risk management measures, such as setting stop-losses, adjusting trading volume and constantly monitoring the market. This can help them minimize losses when prices move against their desired direction and protect their accounts from strong fluctuations.
High frequency trading (HFT) strategies
High frequency trading (HFT) focuses on executing large volumes of orders very quickly, exploiting small price fluctuations or temporary market distortions. HFT systems typically place servers close to the exchange, using powerful hardware and optimized network infrastructure to minimize latency and increase order execution speed.
For example, Nasdaq detects that Apple stock is trading at $175.01 on exchange A but only $175.00 on exchange B. In milliseconds, the algorithm simultaneously buys on exchange B and sells on exchange A, taking advantage of this tiny price difference to profit almost instantly.
Conclude
An algorithmic trading system provides a modern trading approach based on data and intelligent algorithms. Through automation and rapid analysis, the system helps traders seize opportunities, minimize risks, and maintain disciplined trading, laying a solid foundation for long-term market success.