Martingale strategy is a money management technique used to maximize the chances of winning in financial trading. Instead of accepting losses, this strategy aims to balance profits while limiting overall risk. In this article, PF Insight will analyze what Martingale Strategy is and share how to apply it effectively.
- MetaTrader 5 vs cTrader: Which platform is better in 2025?
- Top 5 most common Reversal Candlestick Patterns explained for smart trading
- What is a bullish pattern? 3 high-probability setups every trader should know
What is the Martingale strategy?
Martingale strategy is a betting strategy that works on the principle of doubling the trading volume after each loss to offset the entire previous loss when a winning order appears. This method is often used in situations with a probability of success close to 50%. Although it can help achieve small and steady profits, Martingale requires a large amount of capital and has a very high risk of loss or account burnout.
In situations where the probability of winning and losing is equal, such as a coin toss, traders can choose two different approaches to determining position size. With the Martingale strategy, the position size is doubled after each loss to offset the previous loss when a winning trade occurs. Conversely, the anti-Martingale strategy encourages increasing the position size when winning to maximize profits during a winning streak.
Martingale Strategy illustration example
To understand Martingale trading strategy, you can consider two outcomes that are equally likely: Outcome A and Outcome B. A trader X bets $50 expecting outcome A to occur. However, outcome B actually occurs, causing him to incur an initial loss on that trade.
Using the Martingale strategy, the trader increases the position size to $100 in the hope that outcome A will occur. However, outcome B occurs again, causing him to lose another $100. The position size is then doubled to $200, and the process is repeated over and over again until a winning position is created that completely offsets the previous loss.
It can be seen that when a winning order is achieved, the profit obtained will be greater than the total amount lost in previous transactions. The key point of this method lies in correctly determining the size of the first trading order.
Here are some possible outcomes in the above example:
- Case 1: Trader wins the first order and gets a profit of $50.
- Case 2: Lose the first order but win the second order, the profit from the next transaction will cover the entire initial loss.
-
- Lose $50 on the first order but win $100 on the second order, allowing you to not only recoup your previous loss but also make a net profit of $50.
- Case 3: If you fail the first two orders but win the third order.
-
- You lose $50 on the first trade and then lose another $100 on the second. However, when you win $200 on the third trade, your total profit after covering your losses is $50.
- Case 4: After failing in the first three orders, the trader wins in the fourth order, the trader will recover all the lost capital and get a small profit
-
- You lose $50 on the first trade, $100 on the second, and $200 on the third. But when you get to the fourth trade, your $400 win not only covers all your previous losses but also leaves you with a net profit of $50.
Common types of Martingales in the market
Grand Martingale

The Grand Martingale is a variation of the traditional Martingale strategy. With this method, after each loss, the trader not only doubles the position size but also adds one more unit of capital to the next trade to increase the possibility of recovering all losses and achieving higher profits.
In other words, if you start with 5 orders and that trade loses, the next order will increase to 11 orders (5×2+1). If it loses again, the order size will be 23 (11×2+1). In Grand Martingale, the trader usually sets a maximum limit on the position size, for example 500 units. Then the volume sequence can grow in the following order: 11, 23, 47, 95, 191, 383, which helps to manage the risk within the control range.
After the sixth trade, if you continue doubling, the position size will increase to 767 units – exceeding your limit. Therefore, the limit is set at 383 orders, and at this point, the trader should stop increasing the volume to avoid the risk of going out of control.
The Grand Martingale variation ensures that a losing streak is eventually offset by a single winning trade, resulting in a profit that exceeds the total loss. In this system, the net profit after the streak ends is equal to the initial position value plus one unit for each previous loss.
Reverse Martingale
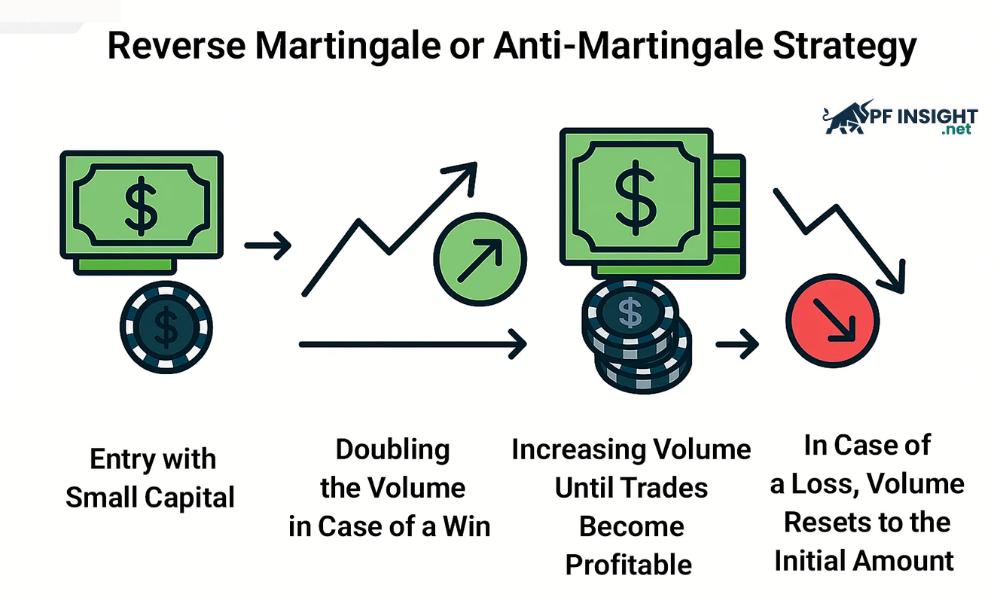
The Reverse Martingale strategy is designed for traders who want to take advantage of winning streaks instead of trying to recover losses. With this method, the trading volume will be doubled after each winning order to maximize profits, and when losing, the trader will return to the original volume to preserve capital and limit risks.
Traders often use both technical and fundamental analysis to assess their ability to maintain a winning streak without exceeding their capital limits. The main goal is to minimize the risk of loss, because just one losing trade can wipe out all previously accumulated profits. Therefore, they always try to control the size of their positions, bringing the trading volume back to the original level after a loss, in order to preserve profits.
Pyramid Martingale
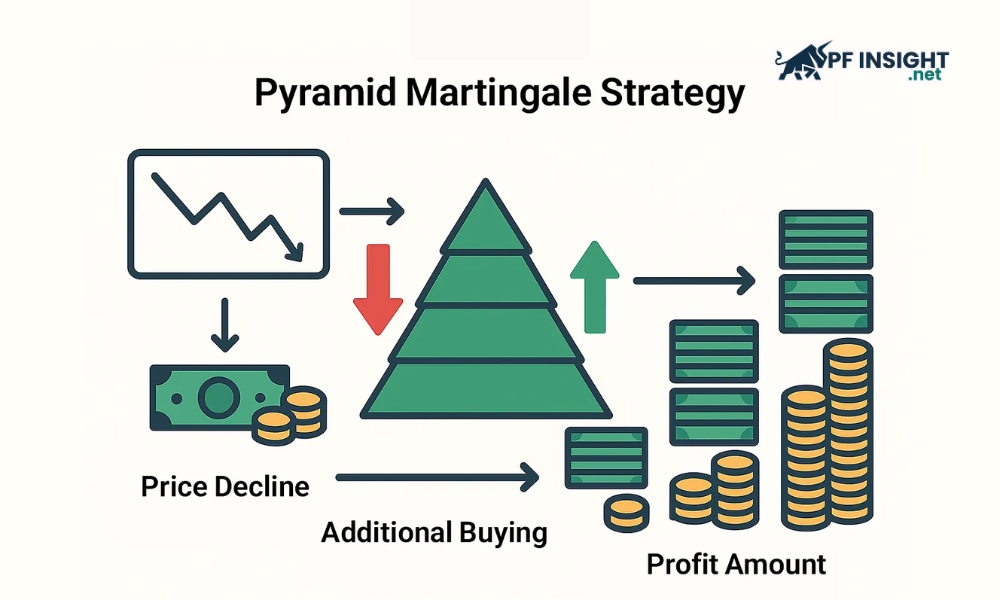
Pyramid Martingale is another variation of the Martingale strategy, which works based on the current market trend. This method involves gradually increasing the deposit amount in a favorable direction, in order to optimize profits as the market continues to move in the expected direction.
In this Martingale variation, the trade size sequence is reset immediately after each win. The main objective is to ensure that at least one unit of profit is made for each winning trade. After each successful trade, the trader reduces the trade size by one unit, believing that the profit achieved is enough to compensate for the previous loss. This method is especially suitable for those who want to trade cautiously, avoiding increasing the order size too much or running on a long losing streak.
Should you use the Martingale method in trading?
To determine whether the Martingale strategy is suitable for your trading style, it is necessary to consider the benefits and risks it brings. While this method can help you recover quickly from losing streaks and generate profits during favorable market periods, the potential risks are also very high. Continuously increasing the volume of orders can easily lead to losses, even wiping out your account without a strict money management plan. Here are the main risks and disadvantages of the Martingale strategy:
Benefits of Martingale
- Flexibility in trading: Martingale strategy can be applied in many different trading environments such as forex, stocks or futures markets. Due to its high adaptability, this method gives traders the flexibility to deploy it on many different assets and market conditions.
- Loss compensation and break-Even: This strategy aims to compensate for losses by continuing to increase the size of the trade until a winning trade is achieved. However, there is no guarantee that good results will appear in real trading.
Ease of Use: Using the Martingale strategy is quite easy as you follow a set of rules until you get the desired results. Although it seems simple to implement, it is still risky and there is no guarantee that you will win. - Helps control and reduce emotional factors: When the market goes down, many traders often lose their composure and rush to exit orders. However, Martingale strategy provides a clear trading rule, helping players stick to the plan, avoid being dominated by fear or “missed opportunity” psychology, thereby making decisions based on specific strategies.
Risks of Martingale
- Risk of exponential losses: The Martingale method carries a huge risk of bankruptcy due to the exponential loss rule. When the losing streak continues, continuously doubling the trading volume requires a large amount of capital. This quickly depletes the account, making this strategy a double-edged sword that can easily lead to a state of no profit.
- The psychological impact of trying to recover losses: Continuously increasing trading volume after each loss can cause traders to fall into a state of stress and lose control of their emotions. The urge to quickly recover losses often leads to impulsive, illogical decisions. This makes them susceptible to falling into a spiral of “revenge trading”, leading to increasingly serious losses.
- Transaction costs and spreads: An often overlooked factor when applying the Martingale strategy is transaction costs and spreads. While it is possible to recover previous losses, executing multiple orders with large volumes will significantly increase the total costs. In highly volatile market conditions, these costs can quickly reduce profits or even turn trading results negative.
Instruct applying Martingale strategy in trading
To use Martingale strategy in trading effectively, you need to follow these steps:

Step 1: Set up trading volume
First, you need to determine the capital you will use for your first trade. It is best to start with a small percentage of your total account balance to reduce risk. Because in the Martingale Strategy, the trading volume will increase after each loss, keeping the initial size small will help you maintain the ability to open more orders without exhausting your capital.
Step 2: Select trading instrument
Once you have completed your market analysis and identified a potential trend, you need to choose the right asset or financial instrument to trade. Choosing the right product, such as currency pairs, stocks or commodities, will help the Martingale strategy work better. The goal is to focus on markets with high liquidity and moderate volatility to minimize risk when doubling the position size.
Step 3: Determine the exact position to open and exit the order
Traders can utilize technical tools such as moving averages, Fibonacci or candlestick patterns to identify potential price zones. Combining multiple analytical elements helps increase the accuracy of trend identification, optimize entry points and take profits or stop losses appropriately, thereby improving the overall effectiveness of the trading strategy.
Step 4: Start executing the command
Execute buy or sell orders at predetermined entry and exit prices. If the trade is profitable, you should return to the original trading volume for the next one. Conversely, if the trade is a loss, apply the Martingale principle by doubling the volume of the next order to cover the loss and maximize the possibility of capital recovery.
Step 5: Repeat the transaction cycle
Maintain the process by doubling the position size after each loss until a profitable trade is achieved. Once the profit appears, return to the original size to control the risk and preserve capital. Strict adherence to this principle helps ensure consistency in the Martingale strategy, while minimizing the risk of a long losing streak, avoiding the risk of depleting the account too quickly.
Step 6: Set stop loss and take profit levels
Always set stop-loss and take-profit orders before entering a trade to control risk and maximize profits. Take-profit orders should be placed near resistance when the market is rising and near support when the market is falling, helping to effectively take advantage of price fluctuations.
Step 7: Track your trade orders
Continuously monitor your trades to ensure they are executed as planned, following the established entry and exit levels. Regular monitoring allows you to make timely adjustments if the market moves unexpectedly, while maintaining discipline and minimizing risk throughout the use of the Martingale strategy.
Step 8: Close the transaction
The final step in applying the Martingale strategy is to close the order when the price moves in a favorable direction, bringing profit. Executing at the right time helps to preserve the accumulated profits while avoiding the risk of adverse fluctuations. Discipline in closing orders is the key factor for the strategy to be effective.
In conclusion, the Martingale strategy can be profitable in stable markets, but it should be applied with caution. Traders should clearly define the level of risk they can bear, set a stop loss order and be willing to accept the risk. At the same time, it should be noted that the risk of losing all capital before a winning order is very high, requiring strict capital management and discipline in trading.
In addition, the Martingale strategy should be applied mainly in markets that are likely to recover from consecutive losing streaks. To take advantage of it effectively, traders need to build a detailed plan, determine the risk level, manage capital properly and adhere to discipline, thereby increasing the chance of compensating for losses and optimizing profits.
Risk management tips for Martingale trading

Martingale strategy in financial trading carries significant risks. Those who apply this strategy need to strictly follow risk management measures to limit losses, and consider the following money management techniques to protect their accounts and maximize profits.
- Determine the appropriate trading volume: Start with a small trading volume and determine the maximum number of times you are willing to double your position. This method helps control risk, protect capital and reduce the risk of serious losses while applying the Martingale strategy.
- Apply stop-loss orders strictly: Setting take-profit and stop-loss levels before entering an order helps limit risks, minimize potential losses and protect the account from strong fluctuations, ensuring safe and controlled trading.
- Fixed percentage risk control: Apply the risk management principle by only risking a fixed percentage of the total account balance for each Martingale order, combined with a maximum stop loss to limit losses and effectively protect capital.
- Diversify your portfolio: Spread your risk across different currency pairs or asset classes, to minimize the negative impact of adverse price movements and increase the stability of your overall trading portfolio.
- Analyze market trends: To effectively protect capital and limit risks, monitor market fluctuations and be ready to adjust operations or stick to the plan when strong trends appear.
Conclude
Although the Martingale strategy can help recover losses quickly, it relies on the assumption of price reversals and stable market conditions. In consecutive losing streaks or strong trending markets, the risk of exponential losses is very high. Therefore, applying Martingale requires careful consideration and careful risk management by the trader before using it.